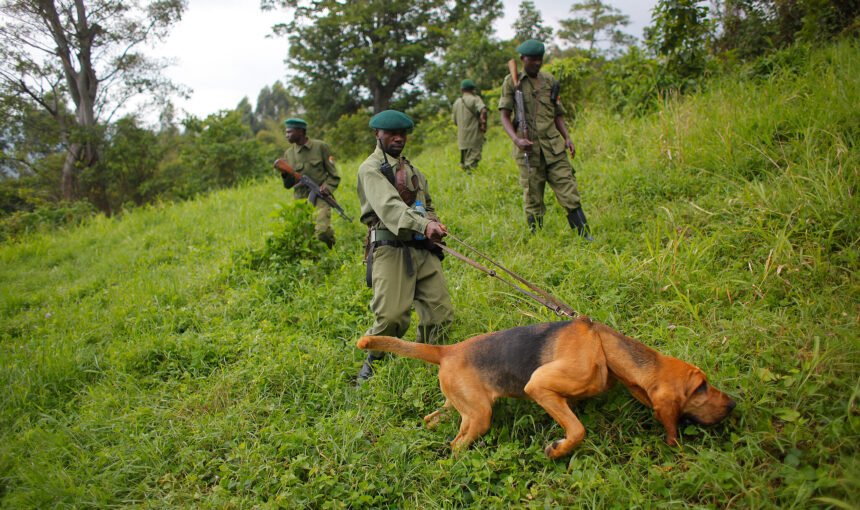
Gorilla Ranger Protection Efforts: Saving Africa’s Last Gorillas 2026
Gorilla Ranger Protection Efforts
Across the mist-covered forests of East and Central Africa, a silent battle is fought every day to protect one of the world’s most endangered species—the mountain gorilla.
At the heart of this battle are gorilla rangers, highly trained frontline conservationists whose protection efforts determine whether gorillas survive or disappear forever.
In 2025, gorilla ranger protection efforts matter more than ever, as human pressure on fragile ecosystems continues to rise.
Thanks to decades of tireless ranger patrols, anti-poaching operations, and community collaboration, mountain gorilla numbers have shown remarkable recovery.
Current estimates place the global mountain gorilla population at just over 1,100 individuals, found only in Uganda, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
While this represents a rare conservation success story, it does not mean gorillas are safe.
Their population remains critically small, isolated, and vulnerable to both natural and human-made threats.
Human activities—such as poaching, illegal logging, agricultural encroachment, and disease transmission—pose constant dangers to gorilla families.
A single wire snare set for antelope can maim or kill a gorilla.
A single human-borne illness can wipe out an entire group.
Against these threats stand gorilla rangers, conducting daily patrols, removing deadly snares, monitoring gorilla health, and intercepting illegal activities before irreversible damage occurs. Without ranger intervention, gorilla populations would decline rapidly.
What makes gorilla ranger protection especially powerful is the human sacrifice behind it.
Rangers operate in dangerous terrain, face armed poachers, endure harsh weather, and risk their lives—often for modest pay—driven by a commitment to protect wildlife that cannot protect itself.
Their courage transforms conservation from an abstract concept into a daily act of heroism.
Today, the future of gorillas depends on sustained ranger protection, responsible tourism, and global awareness.
Every patrol matters.
Every visitor matters. And every conservation decision made today determines whether future generations will inherit a world where gorillas still roam free in the wild.
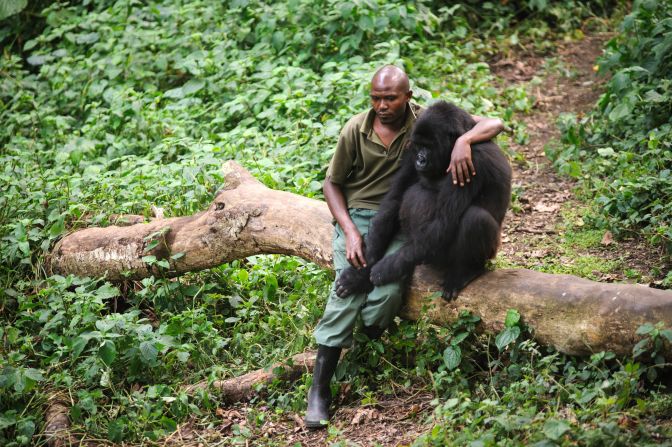

Who Are Gorilla Rangers?
Gorilla rangers are highly trained wildlife protection officers tasked with safeguarding endangered gorillas and the fragile forest ecosystems they depend on.
They form the backbone of gorilla ranger protection efforts, working year-round to prevent poaching, monitor gorilla health, and enforce conservation laws in some of Africa’s most challenging environments.
Unlike general park staff, gorilla rangers are frontline conservation professionals whose daily actions directly determine gorilla survival.
Where Gorilla Rangers Operate
Gorilla rangers operate in a small number of protected areas where mountain gorillas still exist in the wild.
These include Bwindi Impenetrable National Park and Mgahinga Gorilla National Park in Uganda, Volcanoes National Park in Rwanda, and Virunga National Park in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
These forests are dense, mountainous, and often border human settlements, making ranger presence essential for preventing illegal entry, habitat destruction, and wildlife crime.
Gorilla Rangers vs. Gorilla Trackers
Although often confused, gorilla rangers and gorilla trackers play distinct roles.
Gorilla rangers focus on law enforcement, anti-poaching patrols, boundary security, and wildlife protection.
Gorilla trackers, on the other hand, specialize in locating habituated gorilla families for research and tourism purposes.
Trackers support ranger operations by providing movement data, but rangers carry the legal authority to arrest offenders and remove threats within protected areas.
Ranger Training and Selection Process
Becoming a gorilla ranger requires rigorous selection and training.
Candidates are typically recruited from local communities and undergo intensive instruction in wildlife law enforcement, navigation, first aid, firearms handling, ecological monitoring, and emergency response.
Physical endurance, discipline, and commitment to conservation are essential.
Continuous refresher training ensures rangers are equipped to handle evolving threats, from sophisticated poaching networks to emerging wildlife diseases.
Through skill, courage, and dedication, gorilla rangers serve as the last line of defense for one of the planet’s most iconic species.
Why Gorilla Ranger Protection Is Critical
Gorilla ranger protection is critical because mountain gorillas exist on the edge of survival, facing constant and interconnected threats that require daily human intervention.
Without the presence of trained rangers, gorilla populations would rapidly decline due to poaching, habitat destruction, disease, and environmental instability.
Gorilla ranger protection efforts are the primary reason mountain gorillas are still alive today.
Poaching Threats
Although poaching of gorillas is illegal, it remains one of the most serious dangers.
Gorillas are rarely targeted directly, but they often fall victim to wire snares set for other wildlife.
These snares can cause severe injuries, infections, and slow deaths.
Gorilla rangers conduct daily patrols to detect and remove traps, dismantle poaching camps, and arrest offenders before damage occurs.
Their constant vigilance saves countless gorillas from invisible threats hidden within the forest.
Habitat Loss
Expanding human populations surrounding protected areas place immense pressure on gorilla habitats.
Illegal logging, charcoal burning, and agricultural encroachment steadily reduce forest cover.
Rangers enforce park boundaries, prevent land grabbing, and work with communities to reduce forest dependence.
Without ranger enforcement, critical gorilla habitat would disappear within years.
Human–Wildlife Conflict
As forests shrink, gorillas increasingly encounter nearby farms and settlements.
Crop raiding can lead to retaliation, injuries, or deadly confrontations.
Gorilla rangers intervene by monitoring gorilla movements, guiding animals back into protected zones, and educating communities on peaceful coexistence.
Their presence prevents conflict from escalating into fatal outcomes for both humans and wildlife.
Disease Transmission
Gorillas share over 98% of their DNA with humans, making them highly susceptible to human diseases.
Respiratory infections, in particular, can spread rapidly through gorilla families.
Rangers monitor health signs, enforce tourism regulations, and coordinate with veterinarians to isolate and treat sick individuals.
These interventions are essential to preventing population-wide outbreaks.
Climate and Environmental Pressures
Climate change alters rainfall patterns, food availability, and forest health.
Extreme weather increases stress on gorilla populations and disrupts their natural behavior.
Gorilla rangers track environmental changes, protect critical feeding zones, and adapt conservation strategies to ensure gorillas can survive in an increasingly unpredictable environment.
In every threat faced by gorillas today, ranger protection remains the decisive factor between survival and extinction.

Daily Gorilla Ranger Protection Activities
Gorilla ranger protection efforts are not occasional interventions—they are daily, physically demanding, and highly coordinated operations carried out deep inside some of Africa’s most challenging rainforests.
From sunrise to sunset, gorilla rangers work on the frontline to ensure the safety of endangered gorillas and the ecosystems they depend on.
Anti-Poaching Patrols
Anti-poaching patrols form the core of a ranger’s daily duties.
Rangers move in teams through dense forest terrain, often covering long distances on foot.
These patrols aim to:
-
Detect and deter illegal hunters
-
Locate poaching camps and footpaths
-
Confiscate illegal weapons and traps
-
Prevent wildlife crime before it occurs
Their visible presence alone discourages poachers and reduces illegal activity inside protected areas.
Snare Detection and Removal
One of the most life-saving tasks performed by gorilla rangers is snare removal.
Wire snares, often hidden along animal trails, pose a deadly threat to gorillas.
Rangers systematically search known poaching zones and remove:
-
Metal wire snares
-
Rope traps
-
Animal leg-hold devices
Each snare removed represents a gorilla or other wildlife species saved from severe injury or death.
Gorilla Monitoring and Tracking
Rangers closely monitor gorilla families to assess their movements, health, and behavior.
Working alongside trackers and researchers, they:
-
Record gorilla locations using GPS
-
Observe feeding and nesting patterns
-
Identify signs of illness or injury
-
Track group dynamics and population growth
This constant monitoring allows for rapid response when threats or health concerns arise.
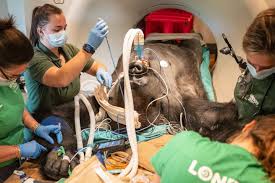
Veterinary Rescue Operations
When a gorilla is injured or falls ill, rangers coordinate with wildlife veterinarians to conduct emergency interventions.
These operations may involve:
-
Securing the area for safe treatment
-
Assisting veterinarians during darting and care
-
Monitoring recovery after intervention
Such rescues have saved numerous gorillas from fatal injuries caused by snares, infections, or human interference.
Forest Boundary Patrols
Gorilla rangers also patrol park boundaries to prevent illegal encroachment.
Their duties include:
-
Monitoring agricultural expansion
-
Preventing illegal logging and charcoal burning
-
Responding to human–wildlife conflict
By maintaining clear boundaries, rangers protect both gorilla habitat and nearby communities.
Intelligence Gathering and Arrests
Beyond physical patrols, rangers gather intelligence through community networks and informants.
This enables them to:
-
Identify organized poaching operations
-
Track repeat offenders
-
Conduct lawful arrests in cooperation with authorities
These proactive measures dismantle wildlife crime networks and strengthen long-term conservation outcomes.
Through these daily activities, gorilla rangers serve as the constant shield between endangered gorillas and the threats that surround them.
Anti-Poaching Strategies Used by Gorilla Rangers
Anti-poaching is one of the most critical components of gorilla ranger protection efforts, requiring a combination of physical patrols, technology, intelligence, and law enforcement collaboration.
Gorilla rangers operate in complex environments where poachers continuously adapt their methods, making strategic, data-driven protection essential.
Patrol Mapping and GPS Tracking
Gorilla rangers use patrol mapping and GPS tracking to plan, record, and evaluate their movements inside protected areas.
Each patrol route is digitally logged, allowing conservation authorities to:
-
Identify high-risk poaching zones
-
Monitor ranger coverage and patrol frequency
-
Adjust deployment strategies based on real-time data
GPS mapping ensures no section of gorilla habitat remains unprotected and helps predict where illegal activities are most likely to occur.
Snare Detection Techniques
Detecting and removing snares requires experience, skill, and local knowledge.
Rangers are trained to recognize subtle signs such as disturbed vegetation, unnatural wire placements, or animal tracks that indicate trap locations.
By focusing on known wildlife corridors and poaching hotspots, rangers significantly reduce the number of injuries caused by hidden traps.
Regular snare sweeps have proven to be one of the most effective methods of preventing gorilla deaths before they happen.
Community Intelligence Networks
Local communities play a vital role in anti-poaching success.
Gorilla rangers work closely with community members who share information about suspicious activities, unfamiliar individuals, or illegal forest access.
This intelligence allows rangers to act preemptively rather than reactively.
By building trust and offering alternative livelihoods linked to conservation, ranger programs transform former poachers into conservation allies.
Technology in Anti-Poaching Operations
Modern gorilla ranger protection increasingly relies on technology.
Rangers use:
-
Two-way radios for rapid communication
-
Surveillance cameras in strategic locations
-
Drones for aerial monitoring in hard-to-access zones
These tools enhance ranger safety, improve response times, and increase detection rates across vast forest areas.
Legal Enforcement Partnerships
Effective anti-poaching depends on strong legal enforcement.
Gorilla rangers collaborate with wildlife authorities, police, and judicial systems to ensure arrested offenders are prosecuted.
This cooperation sends a clear deterrent message that wildlife crime carries serious consequences.
Through these coordinated strategies, gorilla rangers not only stop poaching—but dismantle the systems that enable it.
The Risks & Sacrifices of Gorilla Rangers
Behind every successful gorilla ranger protection effort lies extraordinary personal sacrifice.
Gorilla rangers operate in some of the world’s most dangerous conservation environments, where protecting wildlife often means putting their own lives at risk.
Their courage is rarely seen by the public, yet it is the foundation of every conservation success.
Injuries and Fatalities
Gorilla rangers regularly face serious injuries during patrols.
Dense forests conceal steep ravines, unstable ground, and hidden traps that can cause falls, fractures, or infections.
Tragically, ranger fatalities have occurred during anti-poaching operations, ambushes, and armed confrontations.
Each loss is a painful reminder that conservation comes at a human cost.
Confrontations with Armed Poachers
Many poachers operate in organized groups and carry firearms or machetes.
Rangers frequently confront these armed criminals with limited protection and minimal backup.
Despite the danger, they proceed with patrols, arrests, and confiscations, knowing that hesitation could mean the loss of gorilla lives.
Harsh Terrain and Extreme Weather
Gorilla habitats are rugged and unforgiving.
Rangers trek through thick vegetation, high-altitude forests, heavy rainfall, and extreme humidity.
Patrols can last for days, with limited food, sleep, or shelter.
Physical exhaustion is constant, yet rangers push forward to maintain continuous protection.
The Emotional Toll
Beyond physical danger, the emotional burden is immense.
Rangers witness injured or dead animals, face community pressure, and carry the responsibility of preventing extinction.
The stress of knowing that one missed patrol could cost a gorilla’s life weighs heavily on them every day.
Why They Continue Despite the Risks
What drives gorilla rangers to continue is a deep sense of duty, pride, and connection to the land.
Many are protecting forests their families have lived beside for generations.
They believe that safeguarding gorillas safeguards their own future—and that of the planet.
Their sacrifice transforms conservation from an idea into a lived commitment, deserving global recognition and support.
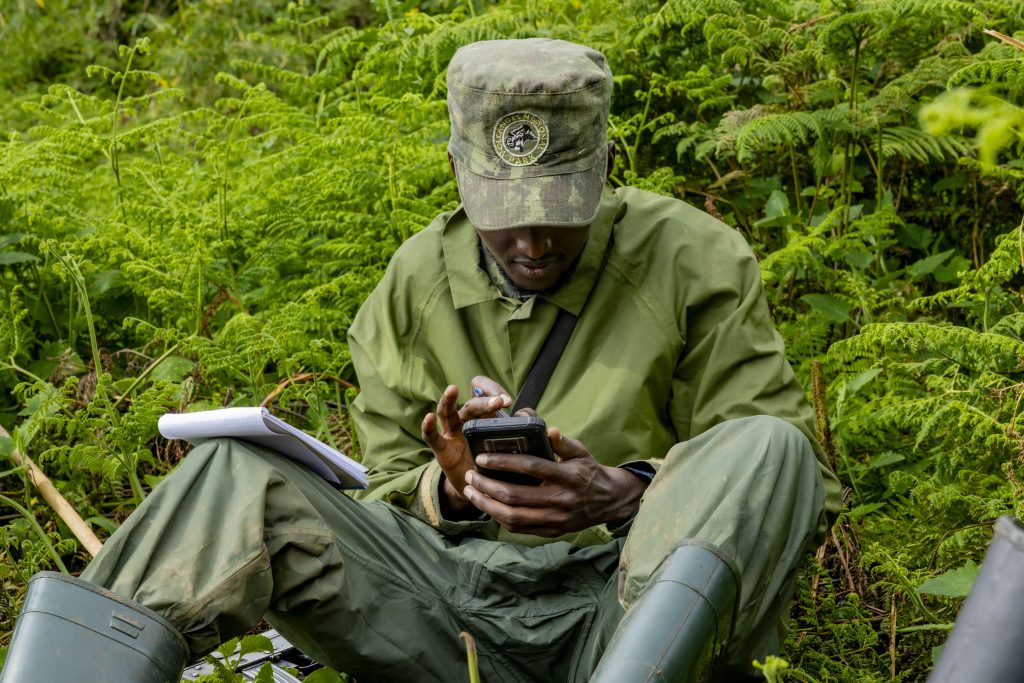

Gorilla Ranger Protection Success Stories
The recovery of mountain gorillas stands as one of the greatest wildlife conservation success stories of the modern era—and at its core are gorilla ranger protection efforts.
While many species continue to decline globally, mountain gorillas have defied the odds thanks to relentless ranger patrols, community cooperation, and sustained conservation funding.
Mountain Gorilla Population Recovery
In the late 20th century, mountain gorillas were on the brink of extinction, with numbers falling below 300 individuals.
Today, conservation surveys estimate the global population at over 1,100 mountain gorillas, found only in Uganda, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
This remarkable recovery is directly linked to continuous ranger protection, anti-poaching enforcement, veterinary intervention, and responsible tourism.
Without daily ranger presence, such growth would not have been possible.
Case Studies from Bwindi and Virunga
In Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, gorilla rangers conduct intensive patrols across rugged terrain, removing thousands of snares annually and closely monitoring habituated and unhabituated gorilla families.
These efforts have stabilized gorilla groups and reduced human-related injuries.
Similarly, in Virunga National Park, one of Africa’s most challenging conservation landscapes, rangers operate under extreme conditions.
Despite political instability and armed threats, Virunga rangers have successfully protected gorilla populations, ensuring their continued survival in one of the world’s most biodiverse regions.
Their work has become a global symbol of conservation bravery.
Rescued Gorilla Stories
Individual rescue stories further highlight ranger impact.
Gorillas injured by snares or suffering from infections have been saved through rapid ranger response and coordinated veterinary care.
Many of these gorillas return fully to their families, continuing to reproduce and strengthen the population.
Each rescue represents a life saved—and a future secured.
The Lasting Impact of Ranger Dedication
The success of gorilla conservation proves one clear truth: when rangers are supported, gorillas survive.
Their dedication transforms conservation funding into real results, turning patrols into protection and effort into hope.
These success stories show that extinction is not inevitable—commitment makes the difference.
Role of Local Communities in Supporting Rangers
Local communities living alongside gorilla habitats are essential partners in successful gorilla ranger protection efforts.
Conservation cannot succeed through enforcement alone; it requires community trust, shared benefits, and active participation.
When local people see tangible value in protecting gorillas, they become the strongest allies of ranger teams.
Revenue Sharing from Tourism
Gorilla trekking tourism generates significant revenue that is shared with surrounding communities.
A portion of permit fees is invested in community projects such as schools, health centers, water systems, and roads.
This revenue-sharing model helps communities recognize that gorilla protection directly improves their quality of life.
As a result, local residents are more likely to support ranger patrols and report illegal activities rather than participate in them.
Education and Employment Opportunities
Education programs play a critical role in long-term conservation success.
Communities receive conservation education that emphasizes the ecological and economic importance of gorillas.
In addition, protected areas provide employment opportunities as rangers, trackers, porters, guides, and lodge staff.
These jobs reduce dependence on forest resources and create sustainable livelihoods linked to wildlife protection.
Community Scouts and Local Intelligence
Community members often serve as scouts or informants, providing valuable intelligence to ranger teams.
Because they understand local terrain and social networks, community scouts can identify unusual movements, suspicious behavior, or emerging threats.
This early-warning system enables rangers to act quickly and prevent poaching before it occurs.
Reducing Human–Wildlife Conflict
Communities and rangers work together to reduce conflict between humans and gorillas.
Measures include boundary monitoring, crop protection strategies, and rapid response when gorillas approach farms.
Education programs also promote nonviolent solutions and coexistence strategies.
By reducing conflict, both human safety and gorilla survival are improved.
When communities benefit from conservation, ranger protection becomes more effective, sustainable, and resilient—ensuring gorillas remain protected for generations to come.
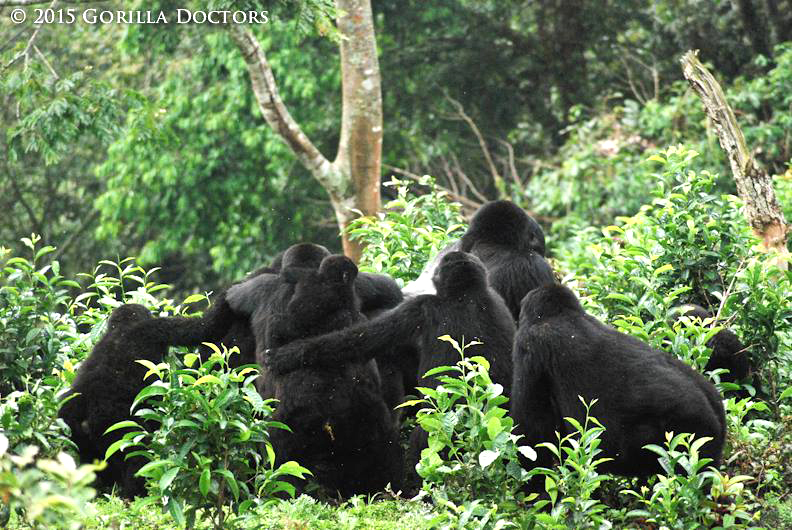

How Gorilla Trekking Tourism Funds Ranger Protection
Gorilla trekking tourism is one of the most powerful tools supporting gorilla ranger protection efforts.
Every trekking permit purchased directly contributes to the survival of mountain gorillas by financing ranger salaries, equipment, training, and long-term conservation programs.
This sustainable tourism model proves that responsible travel can protect wildlife while benefiting local communities.
Permit Fees Breakdown
Gorilla trekking permits are carefully structured to fund conservation.
A significant portion of each permit fee is allocated to park management and ranger operations.
These funds support daily patrols, anti-poaching activities, habitat monitoring, veterinary interventions, and community conservation initiatives.
Additional revenue is reinvested into infrastructure and conservation research, ensuring protection efforts remain effective and well-resourced.
By limiting the number of daily permits, authorities reduce environmental impact while maintaining high conservation value per visitor.
Ranger Salaries, Equipment, and Training
Tourism revenue ensures that gorilla rangers receive regular salaries, which is critical for maintaining morale and professionalism.
Funds are also used to purchase essential equipment such as uniforms, boots, radios, GPS devices, and protective gear.
Ongoing training programs improve ranger skills in wildlife law enforcement, first aid, navigation, and emergency response.
Well-trained and well-equipped rangers are more effective, safer, and better prepared to confront evolving threats.
Why Ethical Tourism Matters
Ethical gorilla trekking follows strict guidelines designed to protect gorillas from stress and disease.
Maintaining safe distances, limiting group sizes, and enforcing hygiene protocols help prevent disease transmission.
Choosing responsible operators ensures that tourism revenue reaches conservation programs rather than causing harm to wildlife.
Unregulated tourism, by contrast, can damage habitats and undermine ranger efforts.
A Sustainable Conservation Model
Gorilla trekking creates a virtuous cycle: protected gorillas attract visitors, tourism funds ranger protection, and strong ranger presence ensures gorilla survival.
This model has enabled mountain gorilla populations to grow while supporting thousands of livelihoods.
Support conservation in action—book responsible gorilla trekking with trusted operator GoSilverback Safaris and directly contribute to protecting endangered gorillas.
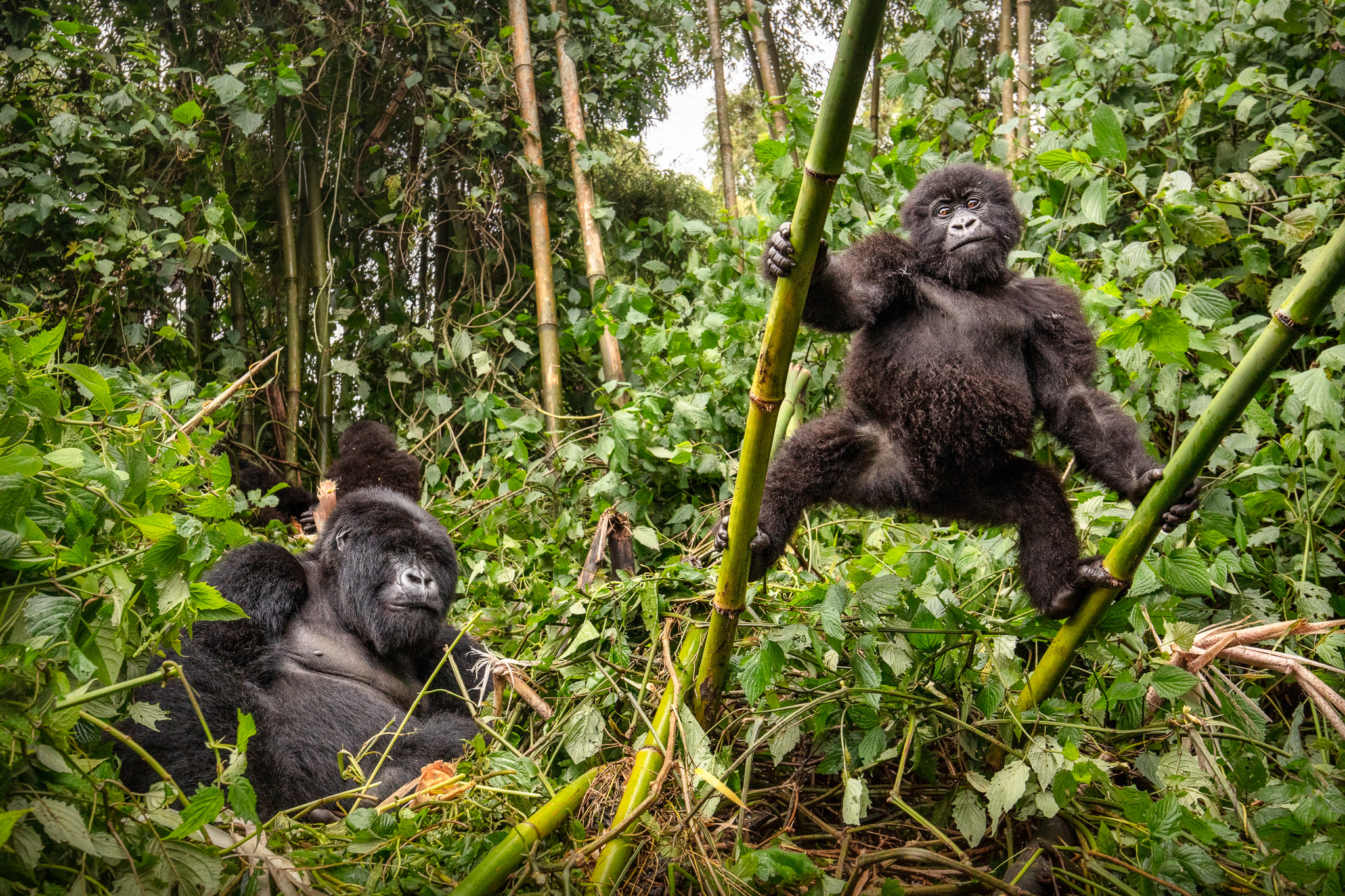

Organizations Supporting Gorilla Ranger Protection
Gorilla ranger protection efforts are made possible through a coordinated network of government agencies, international organizations, and NGOs.
These organizations provide funding, training, oversight, and policy support to ensure that rangers can protect mountain gorillas effectively.
Uganda Wildlife Authority (UWA)
In Uganda, the Uganda Wildlife Authority (UWA) is the primary agency responsible for managing protected areas such as Bwindi Impenetrable National Park and Mgahinga Gorilla National Park.
UWA oversees ranger recruitment, training, and daily patrol operations, while enforcing anti-poaching laws and managing tourism revenue.
Their work ensures that gorilla habitats remain protected and that conservation efforts are sustainable.
Rwanda Development Board (RDB)
The Rwanda Development Board (RDB) manages Volcanoes National Park, home to the iconic mountain gorillas of Rwanda.
RDB organizes ranger patrols, monitors gorilla health, and regulates gorilla trekking tourism.
Their initiatives integrate community development programs to provide local residents with benefits linked to conservation success.
Institut Congolais pour la Conservation de la Nature (ICCN) – DR Congo
In the Democratic Republic of Congo, the ICCN protects gorilla populations within Virunga National Park.
ICCN rangers operate in highly challenging conditions, often facing armed poachers and political instability.
Despite these obstacles, ICCN’s work has helped stabilize gorilla populations and maintain one of Africa’s most biodiverse ecosystems.
NGOs and International Partners
A range of international NGOs and conservation partners support gorilla ranger programs.
Organizations such as the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), and Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund provide training, funding, equipment, and technical expertise.
These partnerships strengthen local ranger capacity, enhance anti-poaching strategies, and raise global awareness of gorilla conservation challenges.
Through the combined efforts of UWA, RDB, ICCN, and supporting NGOs, gorilla ranger protection efforts have become more effective, resilient, and sustainable—offering hope for the long-term survival of mountain gorillas.
How You Can Support Gorilla Ranger Protection
Every individual can play a role in safeguarding mountain gorillas by supporting gorilla ranger protection efforts.
From responsible travel to direct contributions, your actions make a measurable impact on the survival of these endangered animals.
Book Gorilla Trekking
One of the most direct ways to support rangers is by booking gorilla trekking tours through authorized operators.
Trekking permits generate revenue that funds ranger salaries, equipment, anti-poaching patrols, and community projects.
By choosing responsible operators, you ensure that your visit contributes meaningfully to conservation while enjoying a once-in-a-lifetime wildlife experience.
Donate to Ranger Funds
Financial contributions to ranger programs help cover critical needs such as training, medical supplies, protective gear, and emergency interventions.
Many NGOs and conservation organizations offer platforms to donate directly to gorilla ranger funds, allowing you to support frontline conservation even from afar.
Follow Responsible Travel Practices
Responsible tourism helps reduce human impact on fragile gorilla habitats.
Always follow park guidelines: maintain safe distances, avoid leaving litter, and limit group sizes.
Practicing responsible travel minimizes stress and disease risk for gorillas while enhancing the effectiveness of ranger protection.
Spread Awareness
Raising awareness about the challenges faced by gorillas and the dedication of rangers multiplies the impact of conservation efforts.
Share stories, social media posts, and news articles highlighting ranger heroism, population recovery, and ethical tourism initiatives.
Choose Ethical Safari Operators
Not all safari operators prioritize conservation.
Select operators committed to ethical tourism practices, revenue sharing with local communities, and adherence to park rules.
Doing so ensures that your travel dollars directly support gorilla protection and sustainable livelihoods for local people.
By taking these steps—trekking responsibly, donating, educating others, and choosing ethical operators—you become an active partner in gorilla ranger protection efforts and help secure the future of these magnificent animals.

Future of Gorilla Ranger Protection Efforts (2025–2030)
The coming years promise a stronger, more resilient approach to gorilla ranger protection efforts, combining technology, training, and community collaboration to secure the survival of mountain gorillas.
Technology Advancements
Emerging technologies are transforming ranger operations.
Drones, satellite monitoring, GPS-enabled patrol mapping, and mobile communication systems allow rangers to track gorilla movements, detect poaching threats, and respond in real time.
These innovations increase efficiency, reduce risk to rangers, and provide data-driven insights for better conservation decisions.
Increased Ranger Training
Investment in ranger training will continue to be a cornerstone of conservation success.
Advanced courses in wildlife law enforcement, first aid, emergency response, and conflict resolution prepare rangers to face evolving threats from poachers, habitat destruction, and disease outbreaks.
Well-trained rangers are more capable, confident, and effective in protecting gorilla populations.
Community-Based Conservation
Future strategies increasingly emphasize collaboration with local communities.
By integrating education, economic incentives, and participatory conservation programs, communities become active stakeholders in gorilla protection.
Strong community support not only enhances ranger effectiveness but also reduces human–wildlife conflict and ensures sustainable livelihoods.
Hope for Gorilla Survival
With continued global awareness, responsible tourism, and strategic investment, the future looks promising for mountain gorillas.
The combination of skilled rangers, technology, and community engagement provides a robust framework to safeguard gorillas for generations to come.
Every patrol, every rescued gorilla, and every responsible visitor contributes to a growing legacy of conservation success.
The next decade represents a pivotal moment—where dedication, innovation, and partnership can ensure that these magnificent creatures continue to thrive in the wild.
Why Choose GoSilverback Safaris for Your Gorilla Trekking
Choosing the right safari partner can make the difference between a trip that’s forgettable and one that’s truly life‑changing. Here’s why GoSilverback Safaris stands out as the ultimate choice for your Silverback gorilla trekking adventure in Uganda and Rwanda.
1. Expertise That Brings You Closer to the Gorillas
At GoSilverback Safaris, we don’t just book permits — we craft experiences.
Our team includes seasoned trekking guides with deep knowledge of gorilla behavior and the forests’ terrain.
They don’t just lead you — they interpret the jungle, helping you understand gorilla social structures, tracking signs, and how to observe these majestic animals respectfully and safely.
👉 Result: A more immersive, educational, and genuinely meaningful encounter.
2. Committed to Responsible Tourism & Gorilla Conservation
We are not onlookers — we are protectors.
GoSilverback Safaris works hand‑in‑hand with local communities and conservation organizations to ensure that your trek supports the very habitats you came to see.
We emphasize:
-
Respectful, minimum‑impact trekking
-
Community involvement and benefit sharing
-
Revenue going back to protect gorillas and local livelihoods
👉 Your safari becomes part of the solution, not the problem.
3. Safety, Comfort & Personalized Support
Your peace of mind matters.
From the moment you book to the final farewell, we take care of details so you can focus on the wonder of the experience.
We provide:
✔ Pre‑departure briefing and essential trekking advice
✔ Transfer logistics to and from lodges
✔ Porter assistance (optional but very helpful)
✔ First‑aid–trained guides and support staff
👉 You trek with confidence — not worry.
4. Tailored Experiences That Suit Your Style
Whether you’re a seasoned adventurer or a first‑time traveler, GoSilverback crafts itineraries that match your preferences, pace, and budget.
We help you choose:
✨ Ideal trekking zones (Bwindi vs. Mgahinga vs. Volcanoes)
✨ Comfortable or luxury lodge options
✨ Complementary experiences (community visits, nature walks, birding)
👉 This isn’t a one‑size‑fits‑all trip — it’s your journey.
5. Unforgettable Moments Made for You
There’s a difference between seeing gorillas and connecting with them.
With GoSilverback:
-
You get prime positioning in your gorilla encounter
-
Guides help you anticipate and capture the best moments
-
You leave with stories — not just photos
👉 Memories that stay with you long after the safari ends.
Real Support From Real People
We’re not an impersonal booking engine — we’re real people invested in your adventure.
Our client care team is responsive, knowledgeable, and ready to help you every step of the way.
Whether you’re asking about:
📆 Best time to trek
💰 Permit availability and pricing
🛫 Travel planning and packing advice
—we’re here to support you.
In Short — Why GoSilverback Safaris?
Because you deserve more than a tour.
You deserve a meaningful, professionally supported, ethically mindful, and deeply memorable gorilla trekking experience.
👉 Choose GoSilverback Safaris —
where your dream of seeing Silverbacks becomes an unforgettable reality.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many gorilla rangers protect mountain gorillas?
The number of rangers varies by park and country. In Uganda, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo, hundreds of dedicated rangers patrol critical gorilla habitats, ensuring each family group is monitored and protected daily. Their coordinated efforts are crucial to maintaining the growing mountain gorilla population.
Are gorilla rangers armed?
Yes, many gorilla rangers carry firearms or non-lethal protective gear for self-defense against armed poachers. Their role is primarily conservation-focused, but in high-risk areas, being armed is necessary to ensure both their safety and the survival of endangered gorillas.
Do gorilla rangers get paid?
Gorilla rangers receive salaries funded by government wildlife agencies, tourism revenue, and conservation organizations. While compensation varies, additional benefits often include training, equipment, and support for their families, helping sustain morale and commitment to conservation efforts.
How effective are ranger patrols?
Ranger patrols are highly effective in reducing poaching, removing snares, and monitoring gorilla health. Continuous patrols, combined with intelligence gathering and community collaboration, have been instrumental in the recovery of mountain gorilla populations over the past decades.
Can tourists meet gorilla rangers?
Tourists typically meet rangers indirectly through guided gorilla trekking tours, where rangers ensure safety and manage interactions with gorillas. Some parks also offer educational programs or conservation experiences where visitors can learn about ranger duties and the daily challenges of gorilla protection.
Additional Tip
Supporting ethical gorilla tourism and conservation initiatives ensures that rangers have the resources, training, and community backing they need to continue their vital work.
Your visit or donation directly contributes to protecting these incredible animals.
Conclusion
Gorilla rangers are the unsung heroes of Africa’s forests, standing between endangered gorillas and the numerous threats that could wipe them from existence.
From removing deadly snares to monitoring gorilla health, conducting patrols, and collaborating with local communities, their tireless efforts have transformed conservation from a hope into a measurable success.
Thanks to these dedicated rangers, mountain gorilla populations have steadily recovered, demonstrating that human courage and commitment can overcome even the gravest challenges.
Yet, the work is far from over.
Poaching, habitat loss, disease, and climate pressures continue to threaten these magnificent animals.
Each day without sufficient ranger protection increases the risk to gorillas and the fragile ecosystems they inhabit.
The urgency to support ranger programs and ethical conservation practices has never been greater.
Every visitor, donor, and advocate plays a critical role in sustaining these efforts.
By participating in responsible gorilla trekking, donating to ranger funds, or spreading awareness, you directly contribute to the survival of mountain gorillas. Your actions provide rangers with the tools, training, and resources necessary to continue their heroic work.
Support gorilla rangers by booking responsible gorilla trekking or donating today.
Each step you take, each contribution you make, ensures that future generations can witness gorillas thriving in their natural habitats—a living testament to courage, conservation, and human compassion.

